Consultative Selling - the secret to winning complex sales
January 14, 2026
Consultative selling is the ability to uncover and develop a buyer’s true needs—both the obvious and the hidden—and to connect those needs to tailored solutions. It blends curiosity, empathy, and insight with structure and discipline. The best consultative sellers behave like trusted advisors who help customers think more clearly and make better decisions.
Neil Rackham’s SPIN Selling demonstrated that top sellers win not because they pitch harder, but because they ask smarter questions, listen deeply, and create understanding before offering solutions.
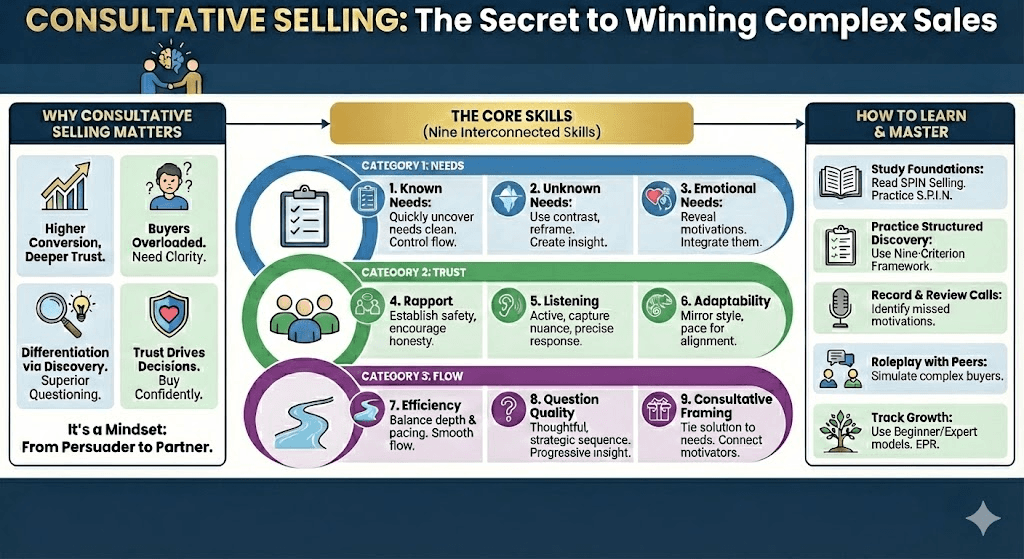
Why Consultative Selling Matters
In complex sales environments, the difference between average and exceptional sellers lies in how well they uncover and clarify buyer needs. A consultative approach drives higher conversion, deeper trust, and stronger long-term relationships.
Buyers are overloaded with information. They need sellers who help them find clarity.
True differentiation happens in discovery. Superior questioning and insight separate experts from order-takers.
Trust drives every decision. When buyers feel understood, they buy faster, more confidently, and at higher value.
Consultative selling is not a tactic; it is a mindset. It transforms sellers from persuaders into partners.
The Core Skills of Consultative Selling
A consultative seller masters nine interconnected skills organized into three categories that mirror the scoring framework: Needs, Trust, and Flow. Each skill can be evaluated at three levels of mastery: Beginner, Intermediate, and Expert.
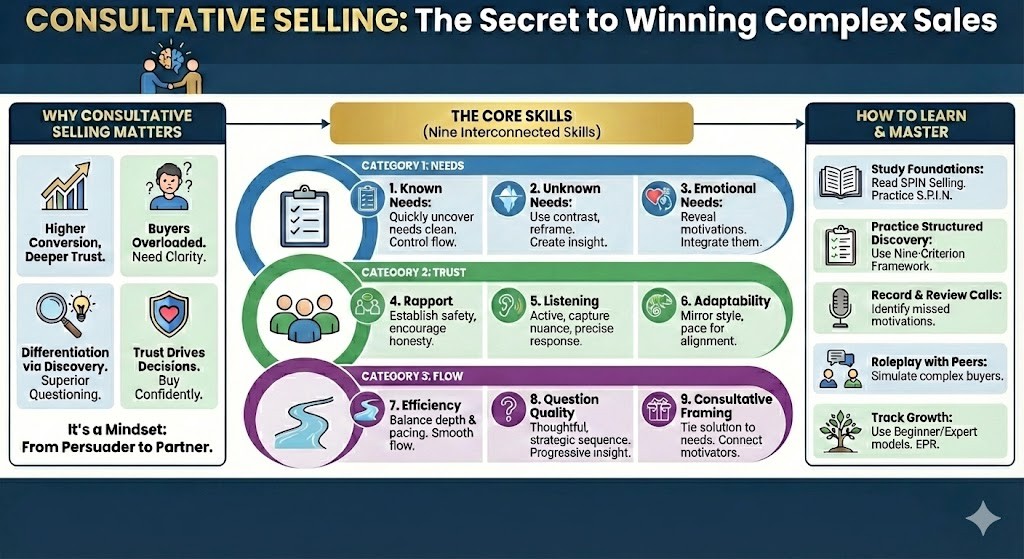
Category 1: Needs – Uncovering and Clarifying What Matters Most
1. Need Discovery – Known Needs
Beginner: Asks surface-level or generic questions and often misses key buyer needs.
Intermediate: Uses structured questioning to uncover most known needs but may repeat or drift off focus. They begin to recognize patterns in buyer responses and connect them to common problem areas but still lack precision in steering the conversation.
Expert: Quickly and elegantly uncovers all known needs through clear, relevant, curiosity-driven questions. They maintain complete control of the conversation flow while making it feel natural to the buyer. Their questioning demonstrates mastery of timing, tone, and phrasing, leading to total clarity on what the buyer truly values.
2. Need Discovery – Unknown or Unarticulated Needs
Beginner: Limits discovery to what the buyer already expresses.
Intermediate: Occasionally triggers new insights but inconsistently. They demonstrate curiosity but lack the deeper question sequencing or confidence to pursue latent motivations once discovered.
Expert: Consistently uses contrast, reframing, or situational probing (as taught in SPIN Selling) to uncover latent or hidden needs and propose thoughtful, plausible hypotheses that surface unspoken motivations. They guide the buyer toward realizations they could not reach on their own. Their approach transforms the conversation from informational to transformational, creating genuine insight and value.
3. Needs Discovery – Emotional and Motivational
Beginner: Focuses on functional features and misses emotional context.
Intermediate: Identifies some emotional drivers but fails to deepen or connect them. They acknowledge emotional hints such as pride or fear but do not yet translate them into actionable insight or positioning.
Expert: Skillfully reveals emotional motivations—such as pride, fear, belonging, or aspiration—and integrates them into the framing of value. They understand that emotion drives logic and use empathy to connect both dimensions seamlessly. Their ability to articulate the buyer’s feelings better than the buyer can creates deep trust and buying confidence.
Category 2: Trust – Building Connection, Safety, and Credibility
4. Rapport and Trust Building
Beginner: Sounds polite but transactional; the buyer remains guarded.
Intermediate: Builds a friendly tone but without deeper rapport. They can engage buyers easily but fail to establish emotional safety or vulnerability that leads to open sharing.
Expert: Establishes authentic trust and emotional safety, encouraging openness, honesty, and genuine collaboration. They make the buyer feel both understood and respected without pressure. Their tone, pacing, and empathy turn a sales conversation into a safe space for candid dialogue.
5. Listening and Responsiveness
Beginner: Listens passively and moves on too quickly.
Intermediate: Occasionally responds to buyer cues but misses emotional signals. They reflect back some buyer statements yet often focus on confirming facts rather than expanding meaning.
Expert: Listens actively, mirrors tone and language, clarifies meaning, and adapts the conversation based on what is heard. They capture nuance in phrasing, pauses, and emotion, responding with precision. Their adaptive listening builds credibility, deepens rapport, and ensures no insight is left unexplored.
6. Adaptability to Buyer Type
Beginner: Applies the same communication style to every buyer.
Intermediate: Adjusts tone or pace inconsistently. They begin noticing buyer personality cues but still default to their own comfort zone rather than fully adapting to the buyer’s decision style.
Expert: Adapts fully—mirroring the buyer’s style, personality, and decision process—to create natural alignment and trust. They adjust pace, vocabulary, and storytelling to match each unique communication profile. This dynamic adaptability makes every buyer feel comfortable and understood, dramatically increasing influence and engagement.
Category 3: Flow – Guiding the Conversation and Framing Value
7. Efficiency and Flow
Beginner: Asks too many disconnected or repetitive questions.
Intermediate: Follows a logical sequence but sometimes loses rhythm. They can maintain a coherent structure but struggle to balance depth and timing, occasionally over-explaining or under-exploring key points.
Expert: Achieves smooth conversational flow, balancing depth and pacing while uncovering key insights efficiently. They know when to probe, when to pause, and when to pivot. The interaction feels effortless for the buyer while the seller maintains full strategic control of direction and outcome.
8. Question Design Quality
Beginner: Asks generic or irrelevant questions that feel scripted.
Intermediate: Shows some structure but lacks progression or insight. They understand the need for strategic sequencing but struggle to maintain flow or relevance between questions.
Expert: Creates a thoughtful question sequence that feels conversational, strategic, and efficient, uncovering both surface and deep needs naturally. They combine curiosity with logic, allowing each question to build insight progressively. Their questioning feels effortless but achieves precise diagnostic depth that differentiates them as true advisors.
9. Consultative Framing of Value
Beginner: Pitches products generically without connecting to buyer needs.
Intermediate: Links features to some known needs but misses emotional ones. They begin to align product benefits with buyer goals but do not yet personalize or emotionally connect the solution to the buyer’s deeper motivations.
Expert: Ties the solution precisely to both stated and unstated needs, positioning value as personal and tailor-made for the buyer. They connect emotional and logical motivators seamlessly, ensuring the buyer sees the offer as the natural solution. Their framing leads to commitment because it transforms the product from a purchase into an answer to the buyer’s story.
Here is a structured performance review to evaluate consultative selling Consultative Sales EPR
How to Learn and Master Consultative Selling
Study the Foundations. Read SPIN Selling and practice Situation, Problem, Implication, and Need-Payoff questions daily.
Practice Structured Discovery. Use this nine-criterion framework to self-score after every call.
Record and Review Calls. Identify where you uncovered needs effectively and where emotional or hidden motivations were missed.
Roleplay with Peers. Simulate buyers with complex motivations and practice adapting tone, pacing, and flow.
Build Curiosity and Empathy. Ask “why” more often and explore not just what the buyer wants but why they want it.
Track Growth. Use the beginner, intermediate, and expert model to measure improvement across each category. Use the Consultative Sales EPR
Conclusion
Consultative selling is the craft of understanding people, not just promoting products. The best sellers diagnose before prescribing, listen before speaking, and reveal before pitching. They create conversations that lead to clarity, confidence, and trust.
A beginner focuses on gathering information.
An intermediate connects questions to insights and begins shaping value through structured conversation. They know what to look for but are still mastering how to guide the buyer toward realization.
An expert reveals meaning, emotion, and value, transforming a sales conversation into a partnership built on understanding and shared goals. They help buyers make better decisions and see new possibilities. Their approach drives loyalty, influence, and sustained long-term success.